## Insomnia (Primary)
### Introduction
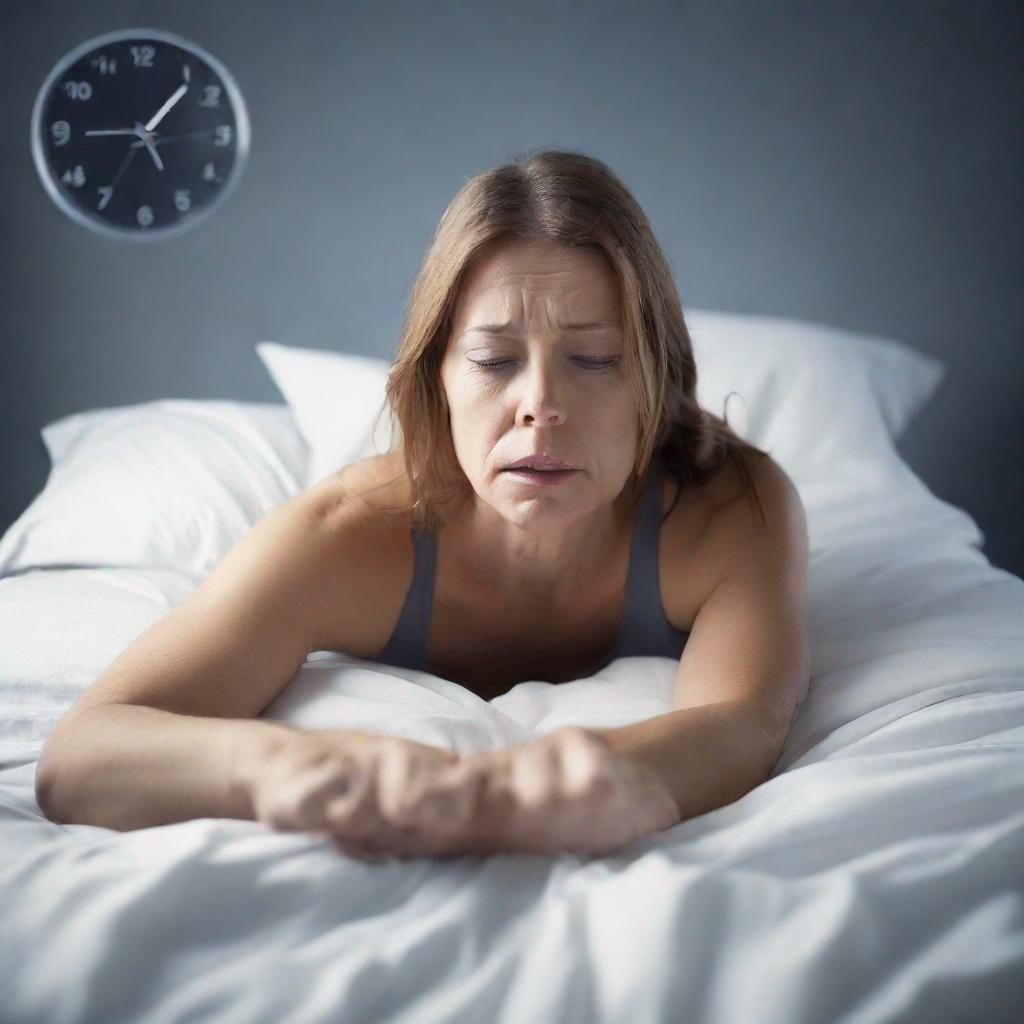
Insomnia is a common sleep disorder that involves difficulty falling or staying asleep. It can range from short-term (acute) to long-term (chronic), and can significantly disrupt an individual’s daily life. Symptoms include non-restorative sleep, excessive daytime sleepiness, and difficulty paying attention.
### Diagnosis
Diagnosing insomnia typically involves a physical exam, sleep history, and sleep study.
**Sleep study (polysomnography):** Measures brain activity, muscle activity, breathing, and heart rate during sleep.
**Multiple sleep latency test (MSLT):** Measures how quickly an individual falls asleep during the day in multiple settings.
**Maintenance of wakefulness test (MWT):** Measures an individual’s ability to stay awake during the day.
### Prevention
Improving sleep hygiene and establishing a regular sleep-wake cycle can help prevent insomnia.
**Sleep hygiene:** Creating an optimal sleep environment (cool, dark, quiet) and avoiding caffeine and alcohol before bed.
**Regular sleep-wake cycle:** Going to bed and waking up at the same time each day, even on weekends.
### Treatment
**Cognitive behavioral therapy (CBT) for insomnia:** A type of talk therapy that focuses on changing negative thoughts and behaviors that contribute to insomnia.
**Stimulus control therapy:** Training patients to associate their bed with sleep only, and not other activities like work or watching TV.
**Relaxation therapy:** Techniques such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing can help reduce stress and promote relaxation before bed.
**Medication:** Prescription and over-the-counter medications, such as benzodiazepines and non-benzodiazepine hypnotics, can temporarily improve sleep. However, they come with potential side effects and may lose effectiveness over time.
### Complications
Untreated insomnia can lead to a variety of complications, including:
* **Physical health problems:** Increased risk of heart disease, stroke, obesity, and diabetes.
* **Mental health issues:** Anxiety, depression, and difficulty concentrating.
* **Social problems:** Conflict with family and friends, decreased productivity at work or school.
### Body Parts and Nervous System Involvement
Insomnia primarily affects the **brain** and **nervous system**. The disruption of sleep neurobiology affects neural circuits responsible for sleep initiation and maintenance.
### Related Terms
* **Sleep hygiene:** Practices that promote healthy sleep.
* **Circadian rhythm:** The body’s natural sleep-wake cycle.
* **Melatonin:** A hormone that helps regulate sleep.
* **Adenosine:** A neurotransmitter that accumulates during wakefulness and promotes sleep.
* **International Classification of Sleep Disorders (ICSD):** A manual that classifies sleep disorders.
* **American Academy of Sleep Medicine (AASM):** A professional organization dedicated to sleep medicine.