Thoracoscopy: A Guide to the Medical Test
Introduction
Thoracoscopy is a medical test that allows doctors to examine the inside of the chest cavity visually. This minimally invasive procedure is used to diagnose a variety of **diseases/conditions**, such as **pleural effusion** and **lung cancer**, and can also be used for **therapeutic** purposes, such as removing fluid or tissue.
Procedure
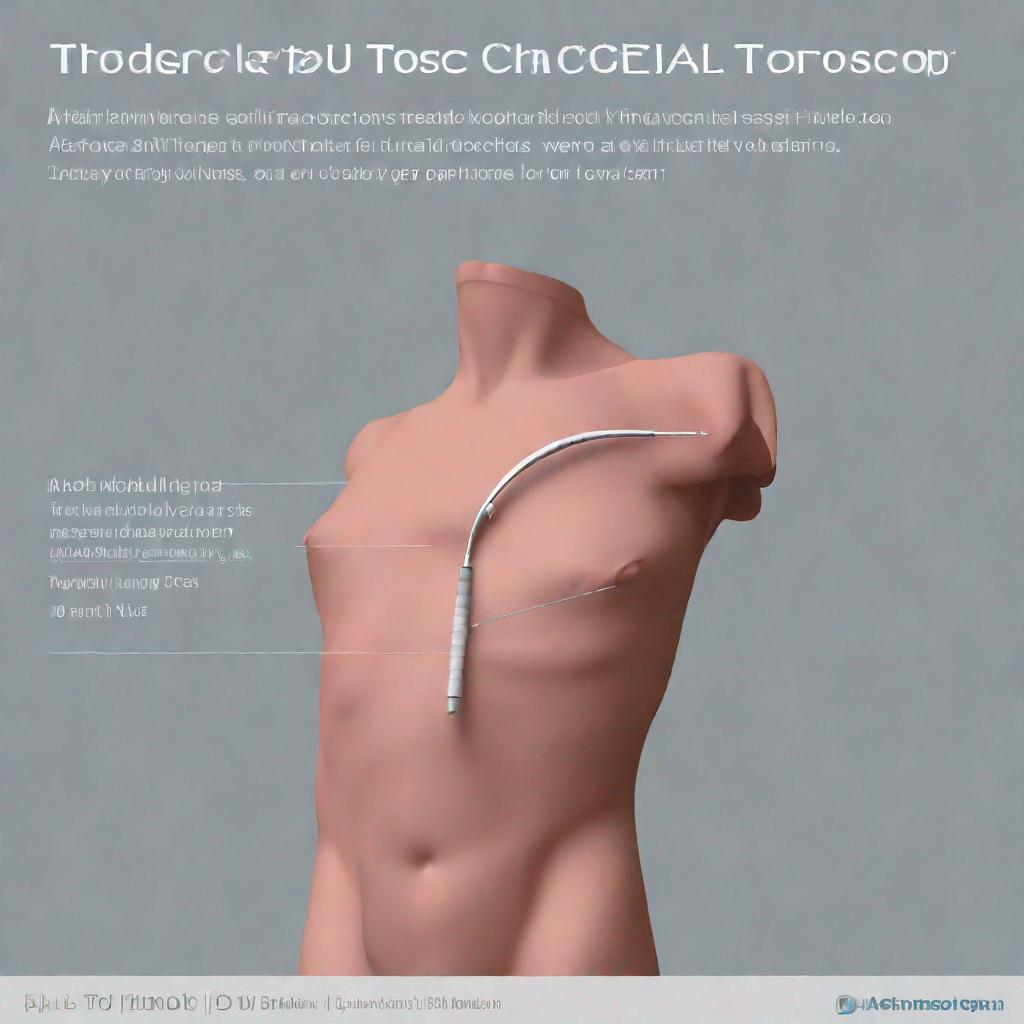
Thoracoscopy is typically performed under **anesthesia**. The doctor inserts a thin, lighted tube called a **thoracoscope** through a small incision in the chest. The thoracoscope contains a camera that sends images to a monitor, allowing the doctor to view the chest cavity in detail.
During the procedure, the doctor may also use instruments inserted through the thoracoscope to perform biopsies, remove fluid or tissue, or repair abnormalities. There are three main types of **thoracoscopy**: medical thoracoscopy, surgical thoracoscopy, and video-assisted thoracoscopic surgery (**VATS**).
Diagnosis
Thoracoscopy can be used to diagnose a variety of **diseases/conditions**, including:
- Pleural effusion: An abnormal buildup of fluid in the space between the lungs and the chest wall
- Empyema: A collection of pus in the pleural space
- Pneumothorax: A collapsed lung
- Hemothorax: A collection of blood in the pleural space
- Lung cancer: Cancer that begins in the lungs
- Mediastinal tumors: Growths that occur in the mediastinum, the area between the lungs
Importance
Thoracoscopy is a valuable tool in diagnosing and treating chest conditions because it allows doctors to:
- Visualize the inside of the chest cavity
- Take biopsies of tissue
- Remove fluid or tissue
- Repair abnormalities
Thoracoscopy is often the best way to diagnose and treat many chest conditions that cause **symptoms** such as **chest pain**, **shortness of breath**, and **cough**. It is also an effective way to remove blood or pus from the chest cavity and to drain pleural fluid.
Alternatives
There are several alternative tests and procedures that may be used to diagnose chest conditions, including:
- Chest X-ray
- Computed tomography (CT) scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan
- Ultrasound
- Bronchoscopy
- Pleural biopsy
- Lung biopsy
The best test or procedure for diagnosing a particular chest condition will depend on the specific condition and the **symptoms** the patient is experiencing. Your doctor can help you decide which test or procedure is right for you.
Preparation
Before undergoing **thoracoscopy**, you will need to follow some simple preparation instructions. These instructions may include:
- Fasting for 8 hours before the procedure
- Avoiding alcohol and tobacco for 24 hours before the procedure
- Taking certain medications as directed by your doctor
- Arranging for someone to drive you home after the procedure
Duration
Thoracoscopy typically takes 30 to 90 minutes to complete, although the length of the procedure will vary depending on the specific condition being diagnosed or treated. You will typically be able to return home the same day as your procedure, but you may need to stay in the hospital overnight for monitoring if you had **surgical thoracoscopy**.
Recommendations
Following **thoracoscopy**, your doctor may recommend that you have additional tests or procedures to confirm a diagnosis or to monitor your condition. These tests or procedures may include:
- Chest X-ray
- CT scan
- MRI scan
- Blood tests
- Follow-up appointments
Your doctor will discuss the results of your **thoracoscopy** with you and will recommend the best course of treatment for your condition.