## The Urea Breath Test: A Non-Invasive Diagnostic Tool for Helicobacter pylori Infection
The urea breath test (UBT) is a non-invasive and highly accurate medical test used to detect the presence of Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) infection in the stomach. H. pylori is a common bacterial infection that can cause a variety of stomach conditions, including gastritis, peptic ulcer disease (PUD), and even stomach cancer.
### Procedure
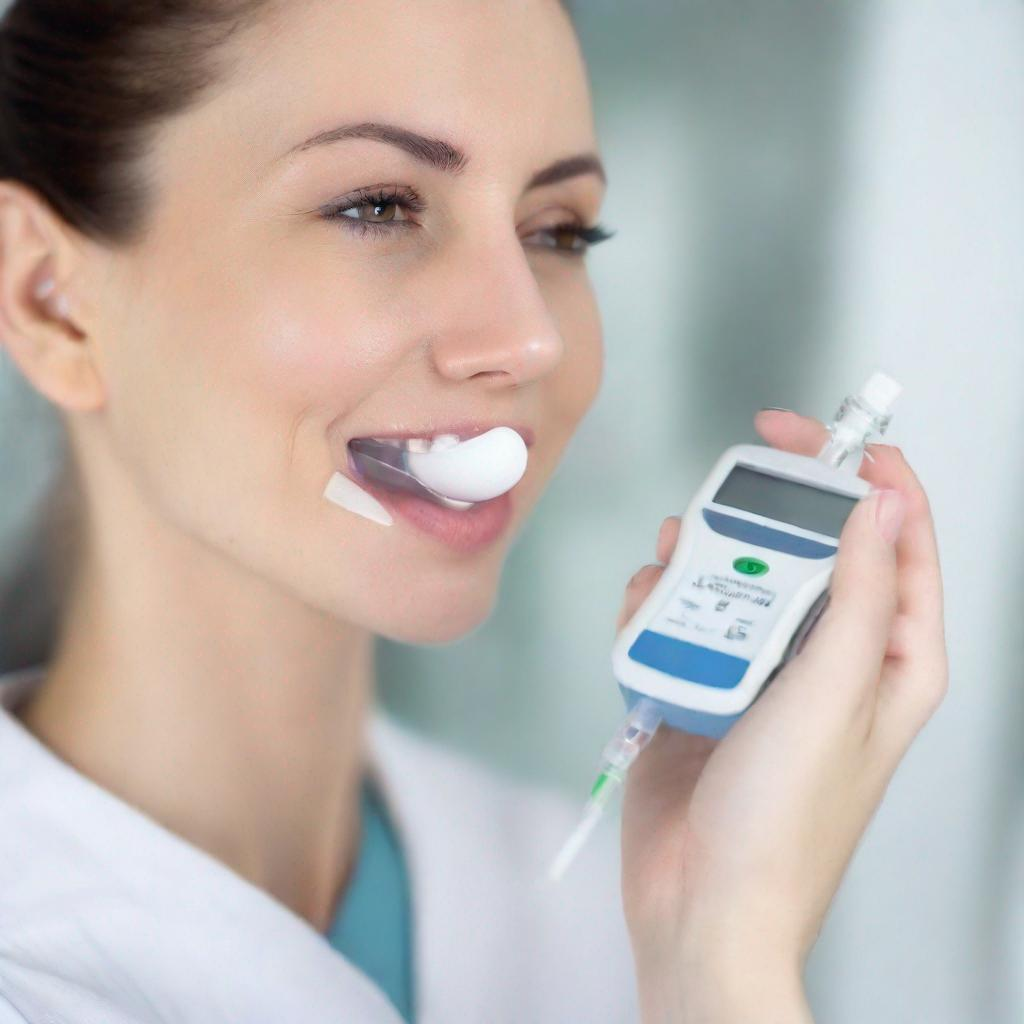
The UBT is typically performed in a medical office or clinic and typically takes less than 30 minutes. The procedure involves the following steps:
1. **Ingestion of Urea Solution:** The patient drinks a clear liquid that contains urea, a compound that is naturally present in the body.
2. **Collection of Breath Samples:** Breath samples are collected from the patient at specific time intervals, usually 10-15 minutes apart. This is typically done by using a special mouthpiece connected to a collection device.
3. **Measurement of Urea Levels in Breath:** The patient’s breath samples are analyzed for the presence of urea. If H. pylori is present in the stomach, the bacteria will break down the urea and release ammonia, which is then absorbed into the bloodstream and exhaled in the breath.
### Diagnosis
A positive UBT result, indicating high levels of urea in the breath, suggests an H. pylori infection. This test has a high sensitivity and specificity for detecting H. pylori, meaning it can accurately identify both infected and uninfected individuals. The UBT is widely accepted as the first-line test for diagnosing H. pylori infection.
### Importance
The UBT is a crucial medical test for several reasons:
* **Non-Invasive:** Unlike endoscopic procedures, the UBT is a non-invasive test, which eliminates the need for uncomfortable or painful procedures.
* **Rapid:** The test is relatively quick and easy to perform, typically taking less than 30 minutes.
* **High Accuracy:** The UBT offers high sensitivity and specificity in detecting H. pylori infection, making it a reliable diagnostic tool.
* **Widely Available:** The UBT is widely available in healthcare settings, making it accessible to patients.
### Alternatives
Alternative tests for diagnosing H. pylori infection include:
* **Endoscopy with Biopsy:** This involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a camera through the mouth to view the stomach lining and take tissue samples for analysis.
* **Stool Antigen Test:** This test analyzes a stool sample for the presence of H. pylori antigens. It is less sensitive than the UBT.
### Preparation
Before undergoing the UBT, patients are usually advised to:
* Fast for at least 4 hours before the test.
* Avoid smoking for at least 30 minutes before the test.
* Inform their healthcare provider if they are taking any antibiotics or other medications.
### Duration
The UBT typically takes around 20-30 minutes to complete. Patients usually receive the results within a few days.
### Recommendations
Following a positive UBT result, patients are usually recommended to undergo antimicrobial therapy to eradicate the H. pylori infection. Proton pump inhibitors may also be prescribed to reduce stomach acid and promote healing. In some cases, endoscopic procedures or surgery may be necessary for treatment.
**Additional Tests:**
* **Gastroscopy:** An endoscopic procedure to examine the stomach lining and take biopsies.
* **Serology:** Blood test to detect antibodies against H. pylori.
* **Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR):** A molecular test that detects H. pylori DNA.