## Abdominal Palpation: A Comprehensive Guide for Medical Diagnosis
### Introduction
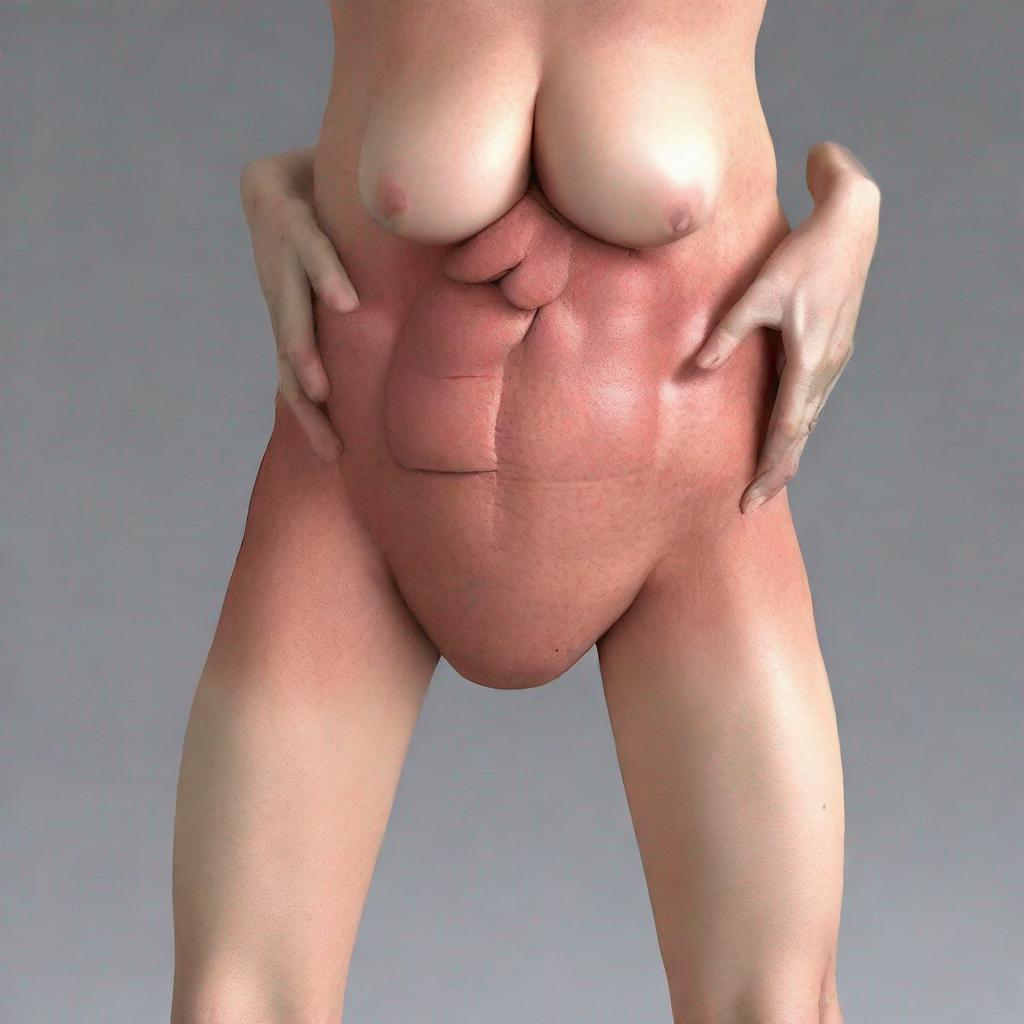
Abdominal palpation is a physical examination technique used to assess the abdomen for any abnormalities or conditions. By manually palpating the abdomen, healthcare providers can identify potential diseases and symptoms that may require further investigation or treatment.
### Procedure
Abdominal palpation is typically performed by a physician or other healthcare professional. The patient is usually asked to lie down on an examination table and expose their abdomen. The healthcare provider then uses their hands to gently press and feel different areas of the abdomen. They may use various palpation techniques, such as:
* **Superficial palpation:** To examine the skin, underlying tissues, and superficial organs.
* **Deep palpation:** To feel deeper structures, such as the liver, spleen, kidneys, and intestines.
* **Percussion:** To tap on the abdomen to assess the size, location, and density of organs.
### Diagnosis
Abdominal palpation can help identify a wide range of conditions and diseases, including:
* Appendicitis
* Bowel obstruction
* Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
* Pancreatitis
* Diverticulitis
* Ascites
* Hernia
* Liver disease
* Kidney disease
* Splenomegaly
* Abdominal mass
By noting the presence or absence of certain signs and symptoms, such as pain, tenderness, guarding, or rigidity, healthcare providers can gain valuable insights into the underlying condition.
### Importance
Abdominal palpation is an essential part of a comprehensive physical examination. It allows healthcare providers to:
* Identify potential medical problems early on
* Monitor the progression or response to treatment
* Guide further diagnostic tests or procedures
* Make informed decisions about patient management
### Alternatives
In some cases, alternative tests or procedures may be used to supplement or replace abdominal palpation, such as:
* **Ultrasound:** Uses sound waves to create images of the abdomen.
* **Computed tomography (CT) scan:** Uses X-rays to create cross-sectional images of the abdomen.
* **Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):** Uses magnets and radio waves to create detailed images of the abdomen.
* **Laparoscopy:** A minimally invasive surgical procedure that involves inserting a small camera into the abdomen.
### Preparation
No specific preparation is required for abdominal palpation. However, it is recommended to wear loose, comfortable clothing and to inform the healthcare provider of any recent abdominal surgeries or injuries.
### Duration
Abdominal palpation usually takes between 5 and 15 minutes. Patients typically receive the results of the examination immediately after it is completed.
### Recommendations
Abdominal palpation is often performed in conjunction with other tests, such as:
* **Auscultation of bowel sounds:** Listening to the abdomen with a stethoscope to assess bowel function.
* **Percussion of abdomen:** Tapping on the abdomen to evaluate the density and size of organs.
By combining these tests, healthcare providers can obtain a more comprehensive understanding of the patient’s abdominal condition.