## Cervical Cancer: Understanding the Disease
### Introduction
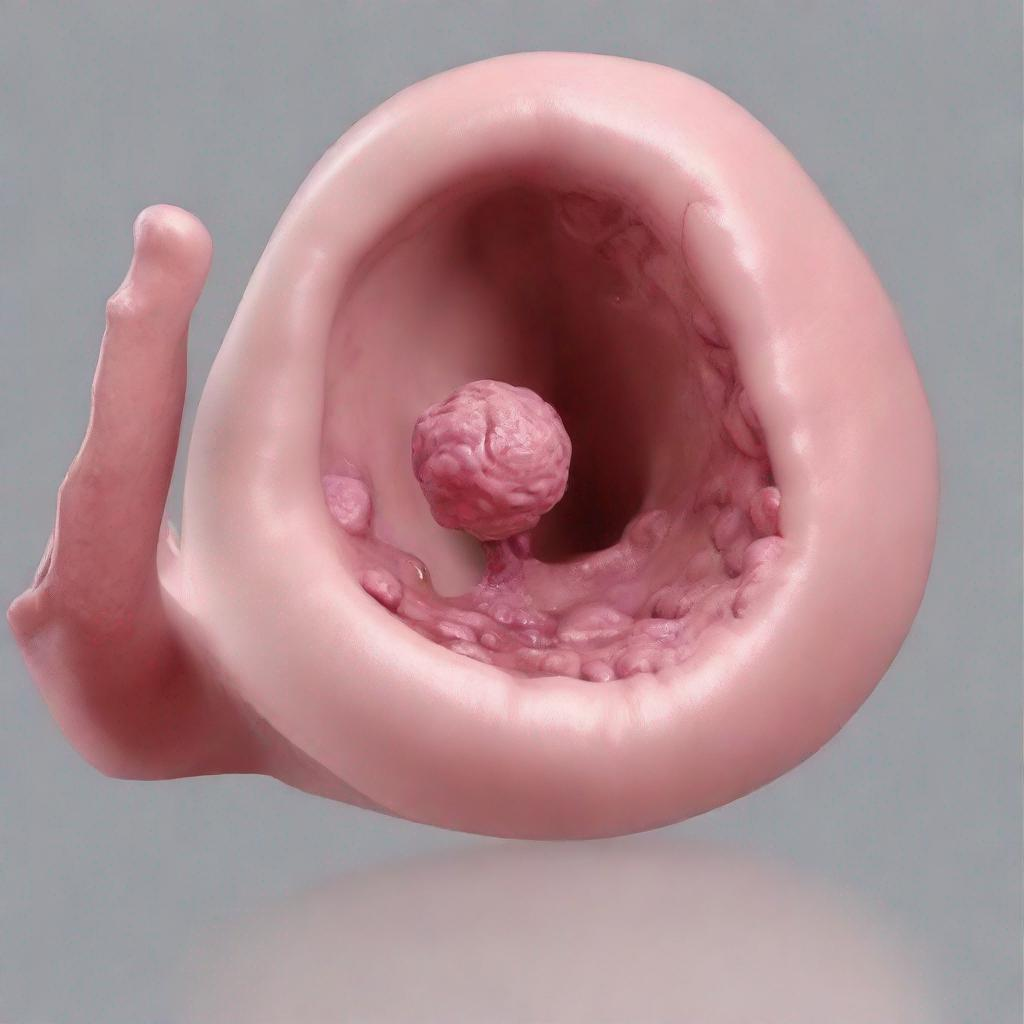
**Cervical cancer** is a type of cancer that develops in the cervix, the lower, narrow end of the uterus (womb) that opens into the vagina. It is the fourth most common type of cancer among women worldwide.
**Symptoms**
* Abnormal vaginal bleeding (after sex, between periods, or after menopause)
* Pain during intercourse
* Pelvic pain
* Vaginal discharge
* Unusual vaginal odor
### Diagnosis and Prevention
Cervical cancer is diagnosed using a variety of tests, including:
* **Pap smear:** Collects cells from the cervix to detect abnormal changes.
* **HPV test:** Detects the presence of the human papillomavirus (HPV), a common cause of cervical cancer.
Prevention of cervical cancer focuses on reducing HPV infection. The **HPV vaccine** is recommended for all girls aged 11 to 12 and women aged 13 to 26.
### Types of Cervical Cancer
* **Squamous cell carcinoma:** The most common type, developing from the thin, flat cells that line the cervix.
* **Adenocarcinoma:** Develops from the glandular cells that produce mucus.
### Stages of Cervical Cancer
Cervical cancer is staged based on its extent:
* **Stage 0:** Precancerous cells confined to the cervix.
* **Stage I:** Cancer confined to the cervix.
* **Stage II:** Cancer extends beyond the cervix but remains within the pelvis.
* **Stage III:** Cancer spreads to nearby tissues or lymph nodes.
* **Stage IV:** Cancer has metastasized (spread) to distant parts of the body.
### Treatment
Treatment for cervical cancer depends on the stage, size, and location of the tumor. Options include:
* **Surgery:** Removal of the cervix, uterus, or surrounding tissues.
* **Radiation therapy:** Uses X-rays to shrink the tumor.
* **Chemotherapy:** Medications that kill cancer cells throughout the body.
* **Targeted therapy:** Uses drugs to block the growth and spread of cancer cells.
* **Immunotherapy:** Strengthens the immune system to fight cancer.
### Complications
Treatment for cervical cancer can result in complications, such as:
* Infertility
* Pelvic pain
* Urinary or bowel incontinence
* Vaginal dryness
### Risk Factors
Factors that increase the risk of cervical cancer include:
* HPV infection
* Multiple sexual partners
* Early age at first sexual intercourse
* Weakened immune system
* Smoking
* Hormonal imbalances
### Outlook (Prognosis)
The prognosis for cervical cancer varies depending on the stage of diagnosis and the individual’s overall health. Early detection and treatment improve the chances of survival.
### Health Literacy and Awareness
**Cervical cancer awareness** is essential to promote screening and early detection. Regular Pap smears and HPV tests are crucial for identifying and preventing cervical cancer. Health literacy and education empower individuals to understand the disease and its risks, making informed decisions about their health.